Mideye 4 RHEL Install
Warning
Mideye Server 4 is no longer updated, and new installations are not supported. Only existing Mideye Server 4 installations and upgrades to latest release are supported. Please use Mideye Server 6 for new installations and continued support.
Introduction¶
This guide describes Mideye Server installation, upgrade and uninstall procedures for Linux servers. This document refers to the Pre-install checklist.
Installation¶
This chapter describes the procedure for a fresh installation of Mideye Server. If a previous version of Mideye Server is already installed, please see the section Upgrade below.
Prerequisites¶
Before executing the Mideye Server installation package you need the following:
- An updated release of CentOS 7.
- A clean database on MySQL dedicated to Mideye.
Root Account¶
In order to install Mideye Server it is necessary to execute the installation package as root.
Obtaining Installation Package¶
Mideye Server installation package can be downloaded here with username and password provided by Mideye Support. Provide your phone number when asking for credentials since the download page is protected with two-factor authentication.
In the Linux folder, you will find installation packages (rpm) for 64 bit (x86_64) operating systems.
Database¶
Mideye Server needs a database that be can installed locally or be hosted on an external server. Supported database servers are listed in the Pre-install checklist. Installing or upgrading Mideye Server requires a database account with rights to ALTER, CREATE and DELETE tables in the Mideye database. Detailed instructions on how to set up the database can be found in the Configuration guide.
Firewall¶
For required firewall openings, please refer to the Firewall section of the Pre-install checklist. It is possible to proceed with the installation steps below while waiting for firewall openings. However, one-time password delivery requires that the server-switch communication is working.
Installation Path¶
The Mideye Server default installation folder is different depending on the operating system architecture. In this document, all the paths referring to the Mideye Server’s installation directory relate to the MideyeServer folder.
For 64-bit Linux operating systems the default path is:
Mideye Server Installation¶
Copy the Mideye Server installation package to the Linux machine and open a terminal in the same folder as the installation package.
Note: If a previous version of the Mideye Server is already installed, please see the section Upgrade below.
For 64-bit platforms, execute the following command:
Mideye Server, as well as all required dependencies, will be installed.
To finalize the installation, the Mideye Configuration tool must be executed, see the next section.
Post-installation Configuration¶
Configuration Tool¶
When the Mideye Server has been installed, execute the following command as root:
Note: if the command is executed from a remote machine through SSH, X-forwarding is needed (adding the -X option to the SSH command). Alternatively, connect with a remote desktop (i.e. using a VNC client/server).
The first time Mideye Configuration Tool is executed, a popup window will inform that the database needs to be configured.
Database not configured 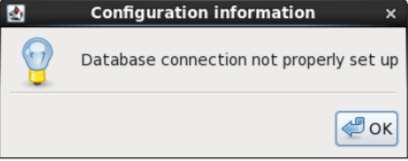
In the Database Connection tab, enter the database credentials (see section ‘Database connection’ in the configuration guide).
Database Configuration
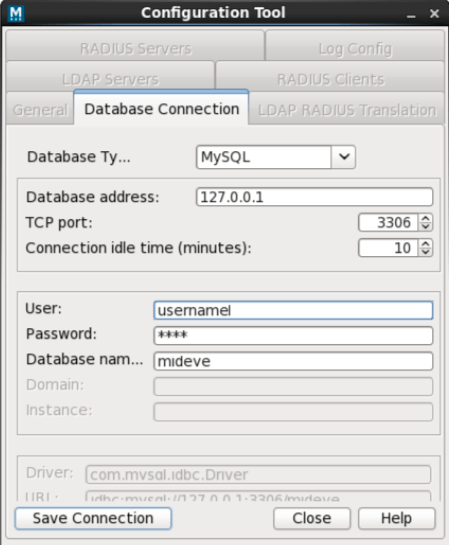
The following dialog will be shown when a connection with the database is established:
Running install scripts on a new database
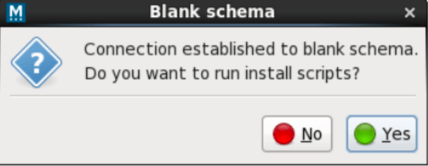
The install scripts have been executed successfully
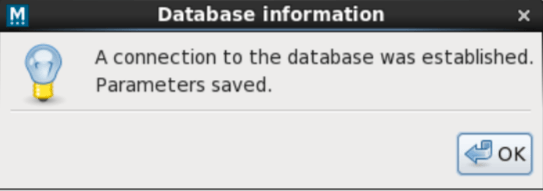
The install scripts will create all the required tables. In order to apply changes, it is necessary to restart Mideye services.
This is done by executing the following command as root:
To check the status of the Mideye Server use the following command:
Note: Other possible commands are stop and start.
BUG: Due to changes in CentOS 7 the tomcat 7 service shows an error on startup. This can be ignored since the service is started correctly. To stop and restart the mideye-webserver service you need to kill it with command: kill -9 <pid>
To get the pid of tomcat use command: ps aux |grep tomcat
Upgrade¶
Upgrading the Mideye Server involves two steps: Executing the installation package, followed by upgrading the database.
Backup¶
Before proceeding with an upgrade, take a backup of the Mideye Server file system and the Mideye database. Some files containing customized settings may need to be replaced after the update.
Mideye Server file system¶
To take a backup of the Mideye Server, copy or compress the whole Mideye Server installation directory. The default directory is:
To copy the entire /opt/mideyeserver folder execute the following two commands:
Database¶
To back up a database on MySQL, run the following command:
where [username]/[password] are the database login credentials.
Upgrade Mideye Server¶
In order to upgrade Mideye Server follow the following steps:
- Download the latest release of Mideye Server and execute the following command:
- Enter database connection parameters (see the ‘Database’ section in Pre-install checklist).
- Click “Save”, then “Close”.
- Restart services by executing the following command as root:
# /etc/init.d/mideyeserver restart
Note: In Configuration Tool, tab “General”, upper left, you can verify that the Mideye Server has been upgraded to the correct version.
Post-upgrade tasks¶
After an upgrade, some files from the pre-upgrade backup may need to be restored:
- Customized log configuration (Syslog, log levels etc):
- Customized SSL port for the administrative web interface:
- SSL certificates for the administrative web interface. Stored in the directory:
- Any custom certificates in:
Uninstall¶
To uninstall Mideye Server run the following command as root:
Uninstallation keeps the database, configuration and log files intact. These can be removed manually by: # rm -rf /opt/mideyeserver
Configuration¶
Further configuration of the Mideye Server can be found in the Configuration guide.
Troubleshooting¶
This section aims to solve common issues that may arise during the installation.
can't Connect to Database¶
Mideye Configuration Tool will not start if a connection to the database can't be established. To solve the problem delete DbConnection.properties located in /opt/mideyeserver/config:
And run Mideye Configuration Tool:
Now you can reconfigure the database with correct settings.